El Niño is a natural weather event that affects countries across the globe. Every few years, this phenomenon causes changes in the climate, leading to unusual weather patterns, such as floods, droughts, and storms. While it might sound complex, understanding El Niño is actually quite simple once you break it down.
In this article, we will explore what it is, how it happens, and why it is important to be aware of its effects.
What Is El Niño?
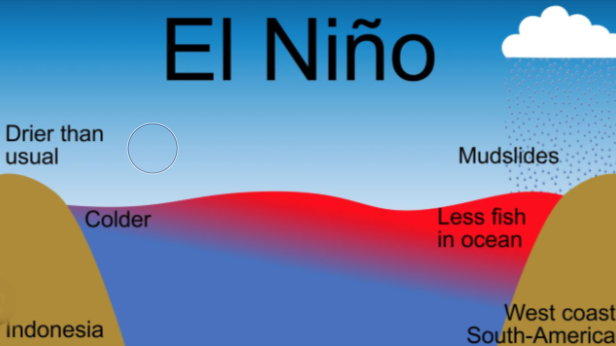
El Niño is part of a climate pattern known as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). It occurs when the surface waters of the Pacific Ocean near the equator become warmer than usual. This warming disrupts the usual weather patterns, leading to extreme weather events in different parts of the world.
Normally, trade winds blow from east to west across the Pacific, moving warm water toward Asia. This pushes cooler water from the deep ocean to the surface near the Americas. During El Niño, these trade winds weaken, and the warm water stays in the central and eastern parts of the Pacific Ocean, near South America. This shift in ocean temperature can have a ripple effect on weather patterns all over the planet.
What Causes El Niño?
Scientists are still studying the exact reasons why El Niño occurs, but they know it is related to changes in the wind and ocean currents in the Pacific Ocean. El Niño tends to happen every two to seven years, lasting for several months, usually starting in late summer or fall and lasting through winter.
While we don’t fully understand what triggers these shifts, modern technology allows scientists to predict when El Niño will happen by observing ocean temperatures and wind patterns. This helps countries prepare for the weather changes that might come.
How Does El Niño Affect the Weather?
El Niño’s effects are far-reaching, impacting countries thousands of miles away from the Pacific Ocean. Some of the most common impacts include:
- Heavy Rain and Flooding: Countries along the Pacific, like Peru and parts of the United States (especially California), often experience heavy rains during El Niño. This can lead to flooding, which damages homes, crops, and infrastructure.
- Droughts: In contrast, some regions, like Australia, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa, suffer from severe droughts during El Niño. Crops can fail, water sources dry up, and wildfires become more common in these areas.
- Warmer Winters: El Niño can also cause warmer-than-usual winters in places like North America. While this might sound pleasant, it can disrupt agriculture and wildlife, which depend on colder conditions during winter months.
- Hurricanes and Typhoons: In some cases, it can also influence the frequency and intensity of hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean and typhoons in the Pacific. However, the effect varies depending on the region.
- Impact on Marine Life: El Niño also affects life in the ocean, particularly around the coasts of South America. During normal conditions, cold water rises from the deep ocean, bringing nutrients that support marine life, including fish. But when El Niño happens, the warm surface water blocks this process, causing a decline in fish populations. This affects the fishing industry and the wildlife that rely on fish as a food source.
https://topnewssurf.com/the-greenhouse-effect/
The Global Impact of El Niño
Although it primarily affects the Pacific Ocean, its influence can be felt around the world. The changes in weather patterns can lead to a chain reaction of events in different regions:
- Agriculture: Farmers can face challenges due to floods or droughts, leading to poor harvests and food shortages. Countries that rely on farming as a major part of their economy may struggle during these periods.
- Health: The weather changes caused by El Niño can also affect public health. In some areas, warmer temperatures can lead to the spread of diseases like malaria and dengue fever, which thrive in warmer, wetter conditions.
- Economic Impact: It can have significant economic consequences, especially in countries that rely on agriculture, fishing, or tourism. Disasters like floods or droughts can damage infrastructure, reduce crop yields, and cause shortages in resources, leading to economic losses.
How Can We Prepare for it?
Because it is a natural event that cannot be prevented, preparation is key. Governments, organizations, and individuals can take steps to reduce its impact by:
- Monitoring Weather Patterns: Advanced technology allows scientists to predict El Niño months before it hits, giving countries time to prepare. Early warnings can help communities brace for potential floods, droughts, or other weather-related disasters.
- Building Resilient Infrastructure: In areas prone to flooding or drought, governments can invest in stronger infrastructure, such as better drainage systems, dams, and water conservation methods, to minimize damage.
- Supporting Farmers and Fishermen: Since agriculture and fishing are often the hardest-hit industries, providing support through crop insurance, training, and alternative livelihoods can help communities recover faster after an El Niño event.
- Raising Awareness: Educating people about it and its potential impacts can help communities better understand the risks and take steps to protect themselves. Simple measures like storing food and water, preparing for emergencies, and listening to weather alerts can make a big difference.
https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/ninonina.html
El Niño may seem like a complex weather phenomenon, but at its core, it is simply a shift in ocean temperatures that has a big impact on global weather patterns. From floods and droughts to changes in marine life and agriculture, its effects are far-reaching.
By understanding how it works and staying prepared, communities can reduce the risks associated with this natural event. Whether you live in a region directly affected by it or not, its influence on the world’s climate makes it something we should all pay attention to.